Cellular System- Basic Concepts
Hai friends in this article let us discuss about some of the basics of cellular system
How they used in olden days?
#)During the olden days a single, high powered transmirtter with antenna was mounted on a tall tower and it used to cover a large service area (as shown in figure below)and the problem due to this method was spectral congestion.

#)Here the service providers could not make use of the spectrum allocationsin proportion to the increasing demand for th emobile services.
#)The radio telephone system was restructutred to achieve high capacity with limited radio spectrum while at the same timecovering very large areas.
The Cellular Concept
#)The cellular cocept was a major breathrough in solving the poblem of spectral congestion and user capacity.
#)It offered ery high capacity in a limited spectrum.
#)In the cellular concept , single high power transmitter is replaced with many low power transmitter seach providing coverage to one small poryion of the service are as shown in the figure below
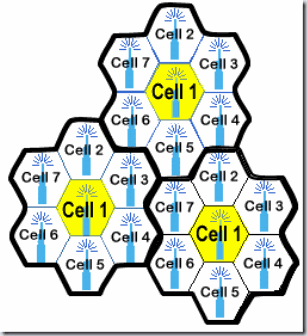
#)Each base station is a allocated a portion,the total number of channels,and nearby base stations are assigned different group of channels.
#)By systematically spacing base stations and their channel groups throughout a market,the available channels are distributed and may be reused as many times as possible or as many times as necessary.
#)The interference between the co channel cells is kept below the acceptance level.
#)As the demand for the service increases, the number of base stations may be increased to provide additional radio capacity with no additional increase in radio spectrum
Frequency Reuse
#)Each cellular base station is alloted a group of radio channels to be used within a small geographic area called cell.
#)The design process of selecting and allocating groups or all the cellular base stations within a system is called frequency reuse or frequency planning.
#)The figure below illustrates the concept of cellular frequency reuse, where cells labelled with the same letter/number use the same group of channels.The picture below the 7 cell reuse pattern where the letter F denotes Frequency

#)Hexagonal geometry is used in the design of a cellular system.
Why we use Hexagonal Geometry in cellular system?
#)the reasons why we use hexagonal shapes are
i)Hexagon permits easy and managable analysis of cellular system.
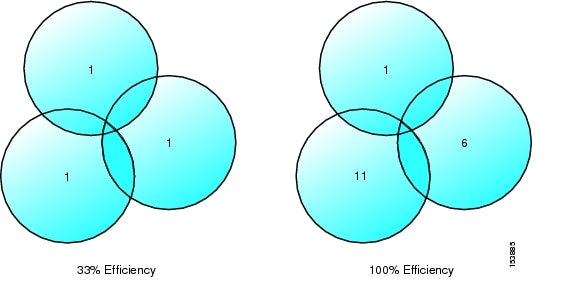
ii)In circular pattern,adjacent circles may leave gaps in between or create over lapping regionsand it is explained in the diagram below

iii)When considering geometric shapes which cover an entire region without overlap or with equal area, there are three choices--a square,an equlateral triangle and a hexagon.
iv)A cell must be designed to serve the weakest mobiles in the service area, and these are typically located at the edge of the cell.For a given distance between the center of a polygon and its farthest perimeter points, the hexagon has the largest area of the three adn therefore by using hexagonal geometry, less number of cells can cover market.
v)Hexagon closely approximates the circular radiation pattern in an omni-directional base station antenna.
#)The actual radio coverage of a cell is known as footprint and is determined from the field measurements or propagation prediction models.
Frequency Reuse........With an example
#)To understand the frequency reuse concept, consider a cellular system which has a toatal of S duplex channels available for use.
#)If each cell is allocated a group of n channels adn if the S channels are divided among N cells into unique and disjoint channel groups which each have the same number of channels, the total number of available radio channels can be expressd as
S=nN
#)The N cells which collectively use the comlete set of available frequencies is called a cluster.
#)If a cluster is repeated m times within the system, the total number of duplex channels C can be used to measure the capacity and it is given by
C=mnN=mS
#)The capacity of a cellular system is directly proportionl to the numbr of times a cluster is repluicated in the service area.
#)The fatcor N is called cluster size.
#)If the cluster size N is small, clusters can be repeated in large numbers and hence more capacity is achieved.
#)But, a small cluster size indicates that cochannel cells are located musch closer together and giving more interference.
#)The value of N is a function of how much interference a mobile or a base station can tolerate while maintaining a good quality
of communication.
#)For maximum capacity, the smalles possible value of N is desirable.
#)1/N is called frequency reuse meter, since each cell within the cluster is only assigned 1/N of the total available channels.
#)the geometry of the hexagon is such that the number of cells per cluster N can only have value which satisfy
wherei,j are non-negative integers.
#)To find the nearest of cochannel cells of a particular cell,
i)move i number of cells in any direction.
ii)turn 60 degrees in counter clockwise direction and move j number of cells.
Channel Assignment Stratergies
#)Channel assignment stratergies can be classified as either fixed or dynamic.
FIXED CHANNEL ASSIGNMENT
#)In fixed channel assignment stratergy, each cell is assigned a fixed number of voice channels.
#)If all the channels are in use, the call is blocked and the subscriber does not receive service.
#)Service variations of fixed assignment startegy exit.
#)One method is borrowing startergy, in whic the cell can borrow channels from neighbouring cell.
#)Mobile switching center(MSC) supervises such procedures and ensures that the borrowing of a channel does not disturb any call in the donar call.The picture below is the that of fixed channel assignment.
DYNAMIC CHANNEL ASSIGNMENT
#)In dynamic channel assignment stratergy, there is no permanent alocation of channels.
#)When a call request is made, the base station requests a channel from MSC.
#)MSC only allocates the channel after verifying that the channel is not presently in use.
#)Dynamic allocation reduces the likelihood of blocking, which increases the trunking capacity of the system, since all the available channels are accessible to all the cells.
#)But it gives extra load to the MSC.The diagram on the right side below is that of the dynamic channel assignment where the channel is assigned dynamically and it is more efficient than that of ficed one shown on the left
Interference
#)Interferene is the major limiting factor in the performance of cellular systems.
#)Sources of interferences are another mobile in the same cell, other base stations operation in the same frequency band,
any non-cellular which leaks energy into the cellular frequency band.
#)Interference on voice channels causes cross talk.
#)Interferences in the control channels lead to missed abd blocked calls.
#)Interference is more severe in urban areas due to the large number of base stations and mobiles.
#)Interference is more severe in urban areas due to the large number of base stations and mobiles.
#)Interference is the major bottleneck in increasing capacity and is responsible of deopped calls.
#)Two major type of cellular interferences are coherent interference and adjacent channel interference.
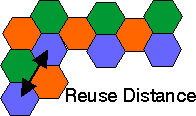
#)In the frequency reuse technique, several cells use the same set of frequencies in the service region.
#)Cells which are using same set of channels are called cochannel cells.
#)The interference between the cochannel cells is called cochannel interference.The picture below illustrates the co channel inteference

#)Interference resulting from the channels which are adjacent in frequency to the desired channel is called adjacent
channel interference.
The role of handover...
#)The process of transferring the call, which is ihn progress from one channel or base stattion to another is alled hanoff or
handover.
#)Priority must be given to handoff requests rather than call initiation requests.
#)The handoff margin "Delta" is defined by,
"Delta"= P(handoff threshold) - (minimum usable)
#)The handoff threshold power is selected such that it is slightly greater than the minimum usable signal for an acceptable voice quality.
#)This margin should not be too large or too small.
#)If it is too large, it may lead to unnecessary handoffs.
#)The call may be headed over to the neighbouring Base Station when the Mobile Station is well inside the home cell.
#)If the margin is too small, the call may die out due to weak signalling conditions before handoff is initiated.
#)The time overwhich a call is maintained within the home cell before handoff is called dwell time.
#)Priority may be given for handoff requests by allocating separate guard channels for handoff purpose.
#)But, this will reduce the overall trafic efficiency.
#)When the call is handed over to another Base Station controlled by a different MSC,which is called intersystem handoff.
#)The handoff in which the channel in the source cell is released and only then the channel in the target cell is engaged hard handoff
#)A handoff in which the channel in the source cell is retained and used for a while in parallel with the channel in the target cell is called soft handoff.The picture below describes the difference between soft and hard handoff.

#)In 1G system all measurements were done at the Base Station.
#)A separate receiver, which is called locator receiver, was used to measure the power from Mobile Station.
#)These radio signal indication values were sent to MSC(Mobile Switching Center).
#)Then MSC will decide handoff is necessary or not.
#)In 2G system,we have Mobile Assisted Handoff(MAHO).
#)Measurements are done at the Mobile Station.
#)When the received power at the Mobile Station from the neighbouring Base Station from the neighbouring Base Station begins to exceed the home base Station, handoff is indicated.
#)We have to ensure that the fall in the power is not due to momentary fading.
#)For that, the power is watched over a period of time and optimum value is taken for initiating handoff.
#)High speed mobiles may require frequent handoff's:pedestrian usrs may not require handoff.
#)This peoblem can be solved by attaching the high speed mobiles to the big cells and slow speed mobiles to micro-cells.
#)The speed of the mobile has to be informed to the company when the user is subscribing a phone.
#)Cell dragging is another problem craeted by a pedestrian user who transmit a very high power to the Base Station and crossing the cell with very slow speed.
#)Some times the power may not fall below the handoff threshold even it is well inside the next cell.#)So, the handoff will
not be initiated.
#)This can be solved by selecting the margin carefully.
These are some of the basic topics which comes under cellular system and friends if u find any mistake please reply....
Like it on Facebook, Tweet it or share this article on other bookmarking websites.

