Art in Middle Age: Modern Era, Contemporary
Art in Middle Age

The vast majority of art that have survived this period falls within the domain of religion and refers to a framework that incorporates both a theological or cosmological and liturgical functions properly. In this aspect strictly religious, it remains necessary to add a social or civic. Thus, a work can be studied and understood in these different aspects: content properly theological speak often by choice iconological from the creators or, a ceremonial liturgical function or concrete will be a physical constraint of the work , sometimes defining its shape, structure or its dimensions, a public exaltation of sponsor, a donor or recipient.
The Art historians classify art medieval periods and key movements, relations between these periods are sometimes more subtle. These are the Celtic Art, Early Christian Art, the Art of migration, the art Pre-Romanesque and Romanesque art, Gothic art, Byzantine art and Islamic art. In addition to this, each "nation" or culture in the Middle Ages had its own artistic style and these are looked at individually, as the Anglo-Saxon art or art Viking.
Medieval art covers a vast scope of time and place, over a thousand years of art history in Europe, the Middle East and North Africa. It includes major art movements and periods, national and regional art, genres, revivals, craft artists, and artists themselves.
Medieval art includes many techniques such as mosaic and sculpture.
Modern Era
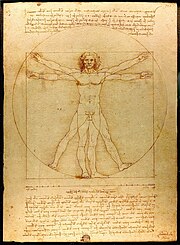 Leonardo da Vinci page sketches on human anatomy
Leonardo da Vinci page sketches on human anatomy
For historians, the modern age - it is sometimes called the "Modern Times" - covers the historical period that begins with the late Middle Ages. Historians are the French end with the French Revolution. This agreement specifically French will not be used in this chapter, in which preferred to use the international convention which will complete the modern era 75 years before the present.
We usually start the Renaissance art in Italy in the fifteenth century . The Italians call this period the Quattrocento. It extends to the sixteenth century where she met while in many countries of Europe, its peak. If she rediscovers mythology and ancient art, yet it does not look back: new technologies, the new political, social and scientific enable artists to innovate. Being rediscovered and it significantly improves the prospect. We developed the technique of oil painting. While in medieval artistic creation was essentially turned towards God and the Christian religion is the man that the artistic Renaissance square in the center of its concerns. For the first time, art enters the private sphere: The works are not only controlled by the religious and secular power, they enter the town houses.

The Ideal City at Urbino long ascribed to Piero della Francesca

Joseph Mallord William Turner The Burning of Parliament, 1835
Usually called "baroque" style which succeeded the Renaissance to the early seventeenth century, but this word was used much later, by authors who found this grotesque style and felt that elements of the ancient art should never have been used otherwise than as Greeks and Romans . Baroque architecture uses more curves and scrolls, she embarked on grandiose, as in the case of the Palace of Versailles to be imitated throughout Europe. The painting uses more color and light. The music of this era emerging opera. The movement reached its apogee in the Catholic Europe of the 1700s.
In the course of the eighteenth century, first in England, one begins to question the habits of classicism. Some connoisseurs seeking to distinguish themselves from others, are looking for originality, especially in the field of architecture that seeks new inspiration even to China and Gothic art. At the end of the century and early next romantic endeavor to restore the feeling against reason: Artists such as Turner evoke, through their representations of nature, the emotions of man against the powers that exceed.

Juan Gris Portrait of Picasso, 1912
This rejection of traditions gives birth to many movements, each of which is decorated like a flag of a new name in "-ism" (realism, naturalism, impressionism, symbolism, ...). It has also resulted in a greater complexity of relationships between artists and buyers of works of art: The artist no longer wishes to adapt to the tastes of its customers. If he does, he may feel to make humiliating concessions. But he prefers working in splendid isolation, it risks being reduced to poverty. Soon some artists come to regard themselves as belonging to a different species and to show their contempt with existing conventions and respectability. In the nineteenth century, the gulf is widening between successful artists and non-conformists, who were especially appreciated after their death .
The Modern Art is born in the late nineteenth and early twentieth century. He sees painting shows the figures of Picasso, Matisse, Miro, Max Ernst and many movements like surrealism, the Oulipo, the New Wave. Architects like Frank Lloyd Wright dare promote the organization of material to the ornamental facades and abandoned the dogma of symmetry .
Alfred Stieglitz, photographed of the Fountain by Marcel Duchamp, 1917.
In France, with modernity, painters stand out gradually from the system and shows the influence of the bourgeoisie. The major contemporary collectors, galleries and critics are important. The art market is becoming.
Marcel Duchamp is the objector founder of conceptual art. It does not relate more to its precursors that his intention is to establish an art object. What he seeks instead is out of art. Yet the readymades of Duchamp (who is the designer) and its kinetic properties bring a new dimension to the aesthetic awareness and an immense contribution to the historiography of modern sculpture, much against his will .
In the field of painting, a decisive step is taken in the 1910s when Kandinsky dares abstract art, which does not represent subjects and objects of the natural world, real or imaginary, but only shapes and colors for them themselves.
At that time, even when they do not give up so dramatically in the representation of a subject, many artists believe that what matters in art is the first form, the subject does come in second . They are in constant search of novelty. With surrealism, they even try to create something more real than reality itself, trying to reach a "higher reality".
Contemporary
The closer we get to our age and it becomes more difficult amid the passing fads of distinguished accomplishments, their influence within the history of art . Some lines of the art of modern times , however, seem to be drawn.
In painting, from the 1950s, some artists are focusing their research on the physical act of painting and carry out works in abstract painting, dripping or throwing color on the canvas. The structure of the table then follows from the intuition of the artist but also the various behaviors of the color (coulures. ..). Paint appears as a moment of unthinking and instinctual life and the work is a testimony of the living body in action and movement in the moment. This movement is called tachism, abstract expressionism or action painting in the United States. The American Jackson Pollock will be specifically noted by this technique. It is reminiscent of Chinese calligraphy in his search for a quick burst and spontaneous.
Many contemporary artists are fascinated by the effects of "texture" and renounce the use of painting for other materials, in productions that are sometimes half-way through painting and sculpture. The Op Art, especially with Vasarely, a particular interest in the interplay of shapes and colors to produce feelings of relief or motion . Closer to home there in the 1960s, pop art uses symbols popular and takes into account the influence of advertising, magazines, comic books and television in consumer societies. By industrial processes, it calls into question the principle of unity of a work of art. As Andy Warhol reproduced endorsed by the hundreds, even thousands.
More generally, contemporary art is crossed by the concepts and topics which agitate modern society: the dematerialization of the work (Yves Klein), deep ecology (Hundertwasser), the visual propaganda and advertising (Warhol) Business artwork or vice versa (Hybert), the fascination with the technological revolution and bio-technology (Eduardo Kac), cosmetic surgery and body re-creation of oneself (Orlan), graffiti, slam, body piercing, rap, etc..

Rome Graffiti
However, the race to novelty and triumph of modernism led the Mavericks to a contradiction: "Should it be non-conformist like everyone else? This may explain that since the late 1970s to a return of figurative and the emergence of a different attitude, more than one (yet) another style, sometimes called post - modernism.
Like it on Facebook, Tweet it or share this article on other bookmarking websites.

